Education is crucial for managing type 1 diabetes, empowering patients with knowledge to control blood sugar levels effectively. Through structured programs and resources, individuals gain insights into treatment, monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. This fosters a lifelong commitment to health, reducing complications and enhancing overall well-being.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease where the pancreas fails to produce insulin, a hormone essential for regulating blood sugar levels. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, individuals with type 1 diabetes cannot naturally control their blood glucose levels, leading to high blood sugar. Symptoms often develop rapidly and include increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, and unintended weight loss. While it is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults, type 1 diabetes can occur at any age. Without insulin therapy, the condition can lead to serious complications, making lifelong management essential.
The Importance of Patient Education in Managing Type 1 Diabetes
Patient education is vital for effectively managing type 1 diabetes, as it empowers individuals to understand their condition and take charge of their health. Through education, patients learn how to administer insulin, monitor blood glucose levels, and adapt their diet and lifestyle to maintain optimal health. Education also helps individuals recognize early signs of complications, such as hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, and take prompt action. By fostering a deeper understanding of diabetes management, education reduces the risk of long-term complications like neuropathy or retinopathy. It also improves adherence to treatment plans, enhances quality of life, and equips patients with the skills to navigate emergencies confidently.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the pancreas stops producing insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. This lifelong condition requires daily insulin therapy.
Causes and Risk Factors
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, halting insulin production. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with certain genes increasing susceptibility. Environmental triggers, such as viral infections, may also contribute to its onset. Risk factors include a family history of diabetes, presence of autoantibodies, and younger age at diagnosis. While the exact cause remains unclear, understanding these factors helps in early detection and management. Education on recognizing symptoms and genetic risks empowers individuals and families to take proactive steps in managing the condition effectively.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of type 1 diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, unintended weight loss, and irritability. If untreated, these can progress to severe complications. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure blood glucose levels and HbA1c, which indicate average blood sugar control over time. Early detection is critical to prevent complications like diabetic ketoacidosis. Patient education emphasizes recognizing these symptoms and understanding diagnostic processes to prompt timely medical intervention. Awareness of these signs enables individuals to seek care early, ensuring proper management and improving long-term outcomes.
Management and Treatment
Effective management of type 1 diabetes involves insulin therapy, blood glucose monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. Patient education focuses on balancing insulin, diet, and exercise for optimal control.
Insulin Therapy and Its Role
Insulin therapy is the cornerstone of type 1 diabetes management, as it replaces the insulin the body no longer produces. Patients require daily insulin administration, typically through injections or an insulin pump, to regulate blood glucose levels. Proper dosing and timing are critical to prevent hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. Education on insulin types—such as rapid-acting, long-acting, and intermediate-acting—is essential for personalized regimens. By understanding how insulin works, patients can align their doses with meals and activities, maintaining stable blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications. Effective insulin management empowers patients to take control of their condition and improve overall health outcomes.

Blood Glucose Monitoring and Control
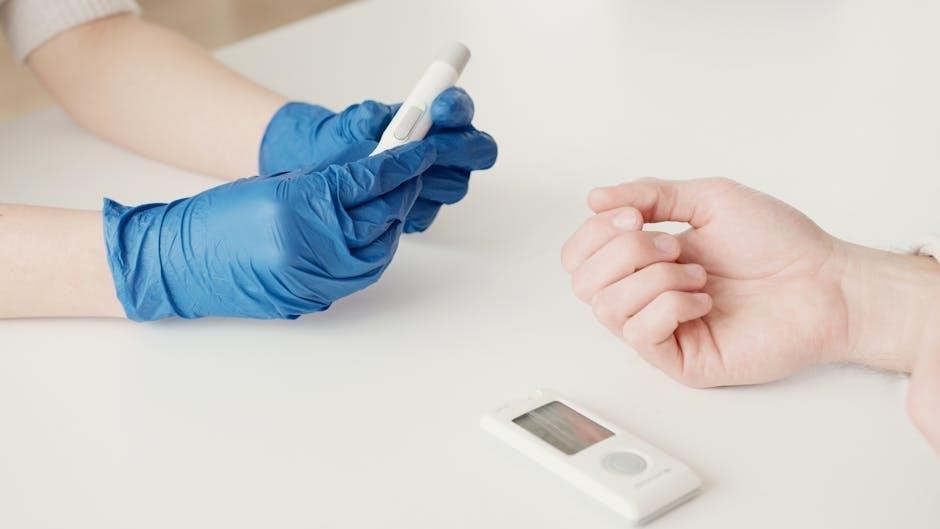
Blood glucose monitoring is vital for managing type 1 diabetes, enabling patients to track their sugar levels and make informed decisions. Regular checks help prevent hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, reducing the risk of complications. Patients typically use glucometers or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) to measure levels throughout the day. Understanding target ranges and how to respond to readings is essential. Monitoring data can guide insulin adjustments, meal planning, and physical activity. Consistent tracking fosters better control and empowers individuals to maintain stable blood sugar levels, improving overall health and quality of life. Educational resources often emphasize the importance of daily monitoring as a cornerstone of effective diabetes management.

Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are essential for managing type 1 diabetes, focusing on diet, exercise, and daily routines to maintain blood sugar balance and overall health effectively.
Diet and Nutrition Planning
A well-structured diet is vital for managing type 1 diabetes, focusing on balanced meals to maintain blood sugar levels. Meal planning should emphasize carbohydrate counting, as carbs directly impact blood glucose. Consistent carbohydrate intake at each meal helps stabilize blood sugar fluctuations. Foods rich in fiber, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats are recommended to slow sugar absorption and provide sustained energy. Avoiding skipped meals and incorporating regular, balanced nutrition helps prevent extreme blood sugar swings. Consulting a dietitian can tailor a plan to individual needs, ensuring proper nutrition while managing the condition effectively.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for managing type 1 diabetes, improving insulin sensitivity, and maintaining overall health. Activities like aerobic exercises (e.g., walking, cycling) help lower blood sugar levels and enhance cardiovascular health. Strength training and flexibility exercises also play a role in building muscle and improving mobility. Before starting any exercise program, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure safety. Monitoring blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise is vital to prevent hypoglycemia. A balanced exercise routine, combined with proper meal planning, helps achieve better blood sugar control and long-term well-being for individuals with type 1 diabetes.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with type 1 diabetes can pose emotional challenges. Coping strategies, counseling, and support systems help individuals manage stress, anxiety, and feelings of isolation, fostering mental well-being.
Coping with Chronic Illness
Coping with type 1 diabetes involves addressing emotional and psychological challenges. Patients often experience anxiety, frustration, and stress due to the constant need for blood sugar management. Developing healthy coping strategies, such as seeking counseling or joining support groups, can help individuals adapt to their condition. Education and awareness empower patients to take control of their health, reducing feelings of helplessness. Building a strong support network, including family and friends, is crucial for emotional well-being. Additionally, setting realistic goals and practicing mindfulness can help manage the psychological burden of living with a chronic illness. Celebrating small achievements can also boost motivation and resilience.
Support Systems for Patients and Families
Support systems play a vital role in helping patients and families manage type 1 diabetes. Educational resources, such as PDF guides, provide essential information on disease management. Online communities and forums offer emotional support and practical advice, fostering a sense of connection among individuals facing similar challenges. Family involvement is crucial, as loved ones can assist with daily tasks like blood sugar monitoring and meal planning. Additionally, healthcare teams, including dietitians and psychologists, offer specialized guidance tailored to individual needs. These support networks empower patients and families to navigate the complexities of type 1 diabetes, promoting resilience and improving overall well-being.

Additional Resources
PDF guides, eLearning courses, and self-care manuals provide comprehensive tools for managing type 1 diabetes, offering detailed insights and practical strategies for patients and caregivers alike.
PDF Guides and Educational Materials
Comprehensive PDF guides and educational materials are essential for type 1 diabetes management. Resources like the Type 1 Diabetes Self-Care Manual and My Life, My Diabetes, My Way series provide detailed guidance for patients, parents, and caregivers. These materials cover topics such as insulin management, nutrition planning, blood glucose monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. Evidence-based reports, such as Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 166, offer in-depth insights into diabetes education. Additionally, Patient Information documents and PDF handouts serve as practical tools for understanding and managing the condition. These resources are widely available online, ensuring accessibility for those seeking to improve their diabetes care and self-management skills.
Online Communities and Forums
Online communities and forums play a vital role in type 1 diabetes patient education, offering a platform for shared experiences and knowledge. Websites like JDRF, Diabetes Mine, and TuDiabetes provide forums where patients and families can connect, ask questions, and learn from others. These spaces foster emotional support and practical advice, helping individuals navigate daily challenges. Additionally, eLearning platforms offer structured courses on self-management, insulin therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Online resources also include webinars, blogs, and downloadable guides, ensuring accessible education. These communities reduce feelings of isolation and empower individuals to take control of their condition, creating a sense of belonging and understanding among those living with type 1 diabetes.

Education empowers type 1 diabetes patients with essential tools for effective management, fostering independence and improving long-term health outcomes through informed decisions and proactive care strategies.
The Impact of Education on Type 1 Diabetes Management
Educating patients with type 1 diabetes significantly enhances their ability to manage the condition effectively. Knowledge about insulin therapy, blood glucose monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments empowers individuals to take control of their health. Studies show that educated patients experience improved blood sugar control, reduced complications, and better overall well-being. Education fosters adherence to treatment plans, promotes early detection of issues, and encourages proactive health decisions. By understanding their condition, patients gain confidence in self-managing their diabetes, leading to a higher quality of life and reduced healthcare costs. Continuous education ensures patients stay updated on the latest advancements, further improving long-term outcomes.
