Anatomy and physiology are scientific disciplines studying the structure and function of living organisms, focusing on the human body. They explore how systems interact to maintain life.
1.1 Definition and Scope
Anatomy and physiology are foundational sciences that explore the structure and function of living organisms, particularly the human body. Anatomy focuses on the physical organization, from cells to systems, while physiology examines how these components function and interact to maintain life. Together, they provide a comprehensive understanding of how the body operates under normal and pathological conditions.
The scope of anatomy and physiology spans various levels of organization, including cellular, tissue, organ, and system levels. It integrates knowledge from biology, chemistry, and medicine to explain mechanisms like metabolism, homeostasis, and feedback systems. These disciplines are essential for fields such as healthcare, research, and education, offering insights into human health and disease.
1.2 Branches of Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and physiology are divided into branches based on investigative techniques, knowledge focus, or body regions. Gross anatomy studies large structures visible to the naked eye, while microscopic anatomy examines tissues and cells. Neuroanatomy focuses on the nervous system, and embryology explores development. Physiology branches into areas like neurophysiology, cardiovascular physiology, and respiratory physiology. Each branch provides specialized insights into body functions, aiding in medical diagnostics and treatments. These divisions ensure comprehensive understanding, from molecular mechanisms to systemic operations. Understanding these branches is crucial for grasping human health and disease, making them fundamental in medical education and research. They collectively contribute to advancing healthcare and biological sciences.

The Human Body: Structure and Function
The human body is organized into hierarchical levels, from cells to systems, each contributing to overall function. Structure and function are interdependent, enabling survival and health.
2.1 Levels of Organization
The human body is organized into six levels of complexity: cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, the organism, and ecosystems. Cells are the basic structural and functional units, forming tissues that specialize in specific functions. Organs, composed of multiple tissues, perform intricate roles, while organ systems integrate these functions to maintain overall health. The organism level encompasses all systems working together, and ecosystems represent interactions with the environment. This hierarchical structure ensures efficiency and adaptability, allowing the body to respond to internal and external changes effectively. Understanding these levels is crucial for comprehending how the body operates as a cohesive unit.
2.2 Body Systems and Their Interactions
The human body consists of 11 major organ systems, each with distinct functions yet highly interconnected. The endocrine system regulates hormones, while the cardiovascular system transports blood throughout the body. The respiratory system provides oxygen, and the lymphatic system supports immunity. The muscular system enables movement, and the reproductive system ensures reproduction. The skeletal system offers structural support. These systems interact to maintain homeostasis, such as the cardiovascular system delivering oxygen from the respiratory system to cells. The digestive system absorbs nutrients, which the circulatory system distributes. The nervous system controls voluntary and involuntary functions, coordinating actions across systems. This integration ensures the body functions as a unified whole, maintaining health and enabling responses to external changes.

Key Concepts in Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomical terminology and homeostasis are foundational concepts. Terminology provides a universal language for describing body structures, while homeostasis ensures the body maintains a stable internal environment through feedback mechanisms.
3;1 Anatomical Terminology
Anatomical terminology forms the foundation of communication in anatomy and physiology. It includes standardized terms describing body structures, directions, and positions. Terms like proximal, distal, and anatomical planes (sagittal, frontal, transverse) are essential. Understanding these terms enables precise descriptions of body parts and their spatial relationships. Directional terms (e.g., anterior, posterior) and body cavities (e.g., thoracic, abdominal) are also critical. This universal language ensures clarity among healthcare professionals and students. Mastering anatomical terminology is vital for identifying and describing structures accurately, facilitating effective learning and application in clinical settings. Study guides often emphasize these terms, providing definitions and visual aids to enhance comprehension and retention.
3.2 Homeostasis and Feedback Mechanisms
Homeostasis is the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. It ensures optimal conditions for cellular functions. Feedback mechanisms regulate homeostasis, with negative feedback reducing deviations and positive feedback amplifying them. For example, temperature regulation involves negative feedback, while blood clotting uses positive feedback. These mechanisms are crucial for health, as disruptions can lead to diseases. Study guides emphasize understanding these processes, as they are fundamental to anatomy and physiology. Mastery of feedback mechanisms aids in grasping how the body responds to stress and maintains balance. This knowledge is essential for diagnosing and treating disorders related to homeostatic imbalances.

Learning Resources for Anatomy and Physiology
Recommended textbooks include Anatomy and Physiology Workbook For Dummies and OpenStax’s free Anatomy and Physiology 2e. Online tools like Anatomy and Physiology Revealed offer interactive learning aids and practice questions.
4.1 Recommended Textbooks and Study Guides
Anatomy and Physiology Workbook For Dummies by Janet Rae-Dupree, offering practical exercises, and OpenStax’s Anatomy and Physiology 2e, a free, comprehensive resource. Study guides like Anatomy and Physiology Revealed provide interactive tools and detailed reviews. The Anatomy and Physiology Nursing Bundle is ideal for healthcare students, while Anatomy and Physiology Made Easy features over 300 illustrations for visual learners. Additional resources include the 50-question study guide covering multiple body systems and a Chapter 8 study guide focusing on muscles. Online platforms like Simple Studies and Lumen offer free PDFs and interactive content, ensuring diverse learning options for students.
4.2 Online Tools and Interactive Resources
Online tools and interactive resources enhance learning in anatomy and physiology. OpenStax offers a free Anatomy and Physiology 2e book with accompanying study guides. Simple Studies provides over 200 free study guides, including Science resources. Lumen’s digital courseware features superior interactivity and multimedia. Platforms like LitRes offer eBooks, such as Anatomy and Physiology Workbook For Dummies, in PDF format. Additionally, free human anatomy worksheets and Google Slides are available for download. Interactive resources like Anatomy and Physiology Revealed and the 50-question study guide aid in exam preparation. These tools cater to diverse learning styles, making complex concepts accessible and engaging for students worldwide.
Clinical Applications of Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and physiology form the foundation for understanding diseases, diagnostic techniques, and treatments. They guide healthcare professionals in clinical practices, ensuring accurate diagnoses and effective patient care.
5.1 Diseases and Disorders
Diseases and disorders often result from malfunctions in anatomical structures or physiological processes. Understanding these abnormalities requires knowledge of normal body functions. Conditions like cardiovascular diseases, respiratory disorders, and neurological impairments can be traced to specific anatomical or physiological failures. For instance, heart diseases often involve issues with blood vessels or cardiac muscles, while respiratory disorders may stem from lung tissue damage. Anatomy and physiology provide the framework for diagnosing and managing these conditions. Study guides detail how structural abnormalities lead to functional deficits, aiding in the development of targeted treatments. By linking anatomical knowledge with physiological mechanisms, healthcare professionals can better comprehend the root causes of diseases and disorders, enabling effective interventions and improved patient outcomes.
5.2 Diagnostic Techniques and Imaging
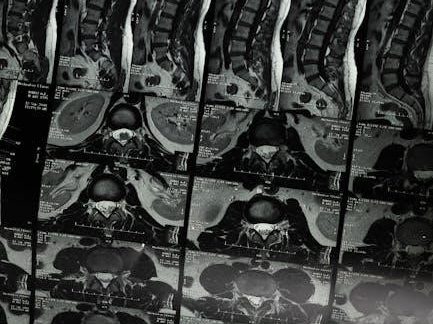
Diagnostic techniques and imaging are crucial for understanding anatomical structures and physiological functions in both health and disease. Tools like MRI, CT scans, and X-rays provide detailed visuals of internal structures, aiding in diagnosis and research. Ultrasound and endoscopy offer real-time insights into organ functions. These technologies are essential for studying anatomy and physiology, as they reveal how body systems interact dynamically. Imaging helps identify abnormalities, such as tumors or fractures, and guides treatments. Study guides often include labeled images and case studies to enhance learning. By mastering diagnostic techniques, students gain practical skills to apply anatomical and physiological knowledge in clinical settings, bridging theory with real-world applications and improving patient care outcomes.
Exam Preparation and Study Tips
Use term lists, learning objectives, and textbook figures to guide your study. Focus on understanding anatomical structures and physiological processes. Start early, practice active learning, and review regularly.
6.1 Effective Study Methods
Effective studying for anatomy and physiology requires a structured approach. Begin by reviewing term lists and learning objectives to identify key concepts. Use textbook figures and resources like Anatomy and Physiology Revealed to visualize anatomical structures. Engage in active learning by labeling diagrams and creating concept maps. Focus on understanding physiological processes rather than memorizing details. Break study sessions into manageable chunks, using flashcards for terminology. Practice answering questions from study guides to reinforce knowledge. Regularly review class notes, PowerPoint slides, and lab manuals. Utilize online tools and interactive resources for hands-on learning. Schedule dedicated time for review to ensure long-term retention and mastery of complex topics.
6.2 Practice Questions and Review Strategies
Practice questions are essential for reinforcing anatomy and physiology concepts. Utilize study guides and textbooks for multiple-choice, true/false, and fill-in-the-blank exercises. Focus on understanding the anatomical basis of physiological processes. Review strategies include categorizing questions by body systems and difficulty level. Regularly test yourself to identify weak areas. Use flashcards for terminology and concepts. Engage in group discussions to clarify doubts. Refer to diagrams and illustrations to visualize structures. Schedule periodic reviews to ensure retention. Incorporate active recall by summarizing key points in your own words. Leverage online platforms and interactive tools for dynamic assessments. Consistency and repetition are key to mastering complex topics in anatomy and physiology.